Quantum Metaphysics
Exploring the philosophical implications of quantum mechanics
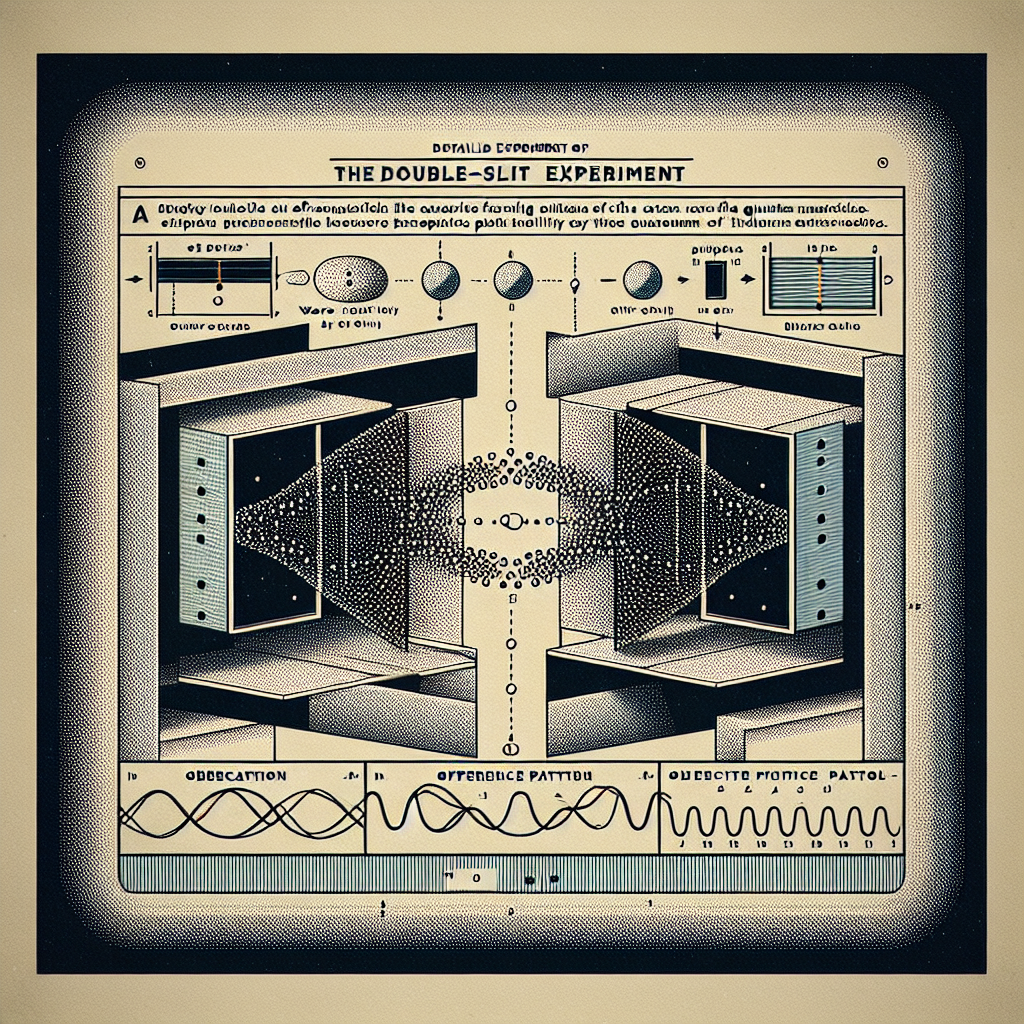
Introduction
- Emergence as physicists and philosophers grappled with strange findings of quantum experiments
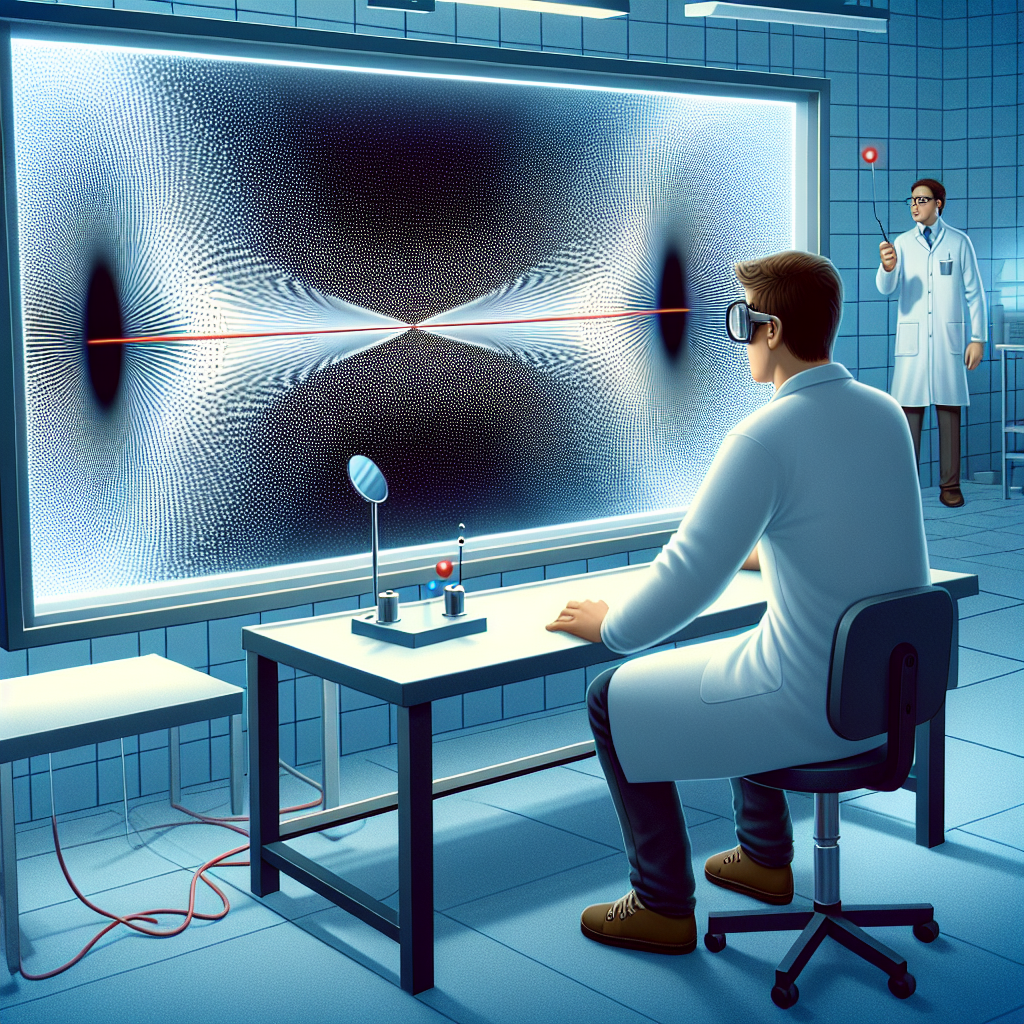
- Phenomena such as superposition and entanglement raise metaphysical questions
Interpretations of Quantum Mechanics
- Copenhagen interpretation
- Many-Worlds interpretation
Challenging Notions of Reality
- Quantum mechanics challenges the notion of an objective reality
- Suggests a link between consciousness and the physical world
Mind-Matter Relationship
- Implications for the mind-matter relationship
- Debate on free will versus determinism
Unified Theory
- Physicists working towards unifying general relativity with quantum mechanics
Worldview and Ethics
- Quantum metaphysics can influence our worldview
- Considerations for ethics
Conclusion
- Summary of key points
- Invitation for questions and discussion